How to make clove oil at home- making clove oil at home can be a rewarding and natural way to explore its potential benefits. Learn the process, precautions, and how to make the most of this DIY remedy.

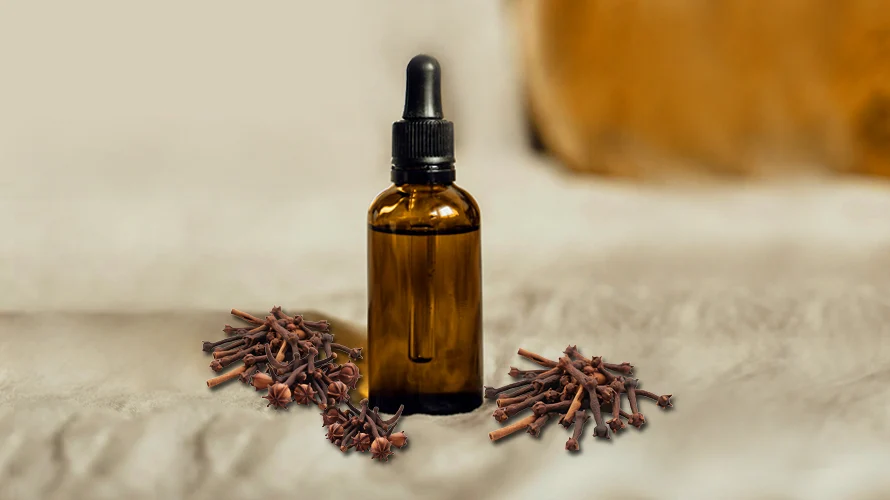
Clove oil, derived from the aromatic flower buds of the clove tree, is renowned for its diverse range of health benefits. Packed with the active compound eugenol, clove oil exhibits potent anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial properties. This natural powerhouse is widely recognized for its ability to alleviate dental discomfort, making it a popular remedy for toothaches and gum issues. Beyond oral health, clove oil’s antioxidant content contributes to overall immune system support and helps combat oxidative stress in the body. With its pleasant, warm aroma, clove oil is also utilized in aromatherapy to promote relaxation and relieve stress. This versatile essential oil stands out not only for its aromatic qualities but also for its potential contributions to oral care, immune support, and holistic well-being.
Origin of Cloves:
Cloves have a long history and originate from the Maluku Islands in Indonesia. The tropical climate of these islands provides an ideal environment for clove trees to thrive. Historically, cloves were highly prized and became a major commodity during the spice trade.
Nations that Use Cloves Most:
Culinary and medicinal uses have made cloves a staple in various global cuisines and traditional healing practices. Nations across Asia, the Middle East, and parts of Africa frequently incorporate cloves into their recipes. Cloves are prevalent in Indian, Middle Eastern, and Indonesian cuisines, where they add a warm, aromatic flavor to both sweet and savory dishes. In many cultures, cloves are also utilized for their potential health benefits, including their analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, often used in natural remedies.
Nations that Produce Most Cloves:
Indonesia is the world’s largest producer of cloves, particularly coming from the Maluku Islands and Sulawesi. Other significant producers include Madagascar, Zanzibar (Tanzania), and India. These countries have favorable climates for cultivating clove trees, allowing for substantial production and contributing significantly to the global spice market.
Cloves have played a crucial role in trade and cultural exchanges, and their influence extends far beyond their region of origin. Their aromatic and flavorful properties continue to make them a valued spice worldwide.
How to Make Clove Oil at Home:
Making clove oil at home is a relatively simple process. Here’s a basic recipe:
Ingredients:
- Whole cloves (about 1/4 to 1/2 cup)
- Carrier oil (such as olive oil or coconut oil)
Instructions:
- Gather Materials: Ensure you have whole cloves and a suitable carrier oil.
- Crush the Cloves:Crush the whole cloves using a mortar and pestle or by placing them in a plastic bag and gently tapping them with a rolling pin. This helps release the natural oils.
- Combine Cloves and Carrier Oil: In a clean, dry glass jar, combine the crushed cloves with the carrier oil. The ratio can vary, but a common guideline is about 1/4 to 1/2 cup of crushed cloves for every cup of carrier oil.
- Mix Well: Stir the mixture thoroughly to ensure the crushed cloves are well distributed in the oil.
- Infuse the Mixture: Seal the jar tightly and place it in a warm, dark place to allow the mixture to infuse. Let it sit for at least a week, shaking the jar daily to enhance the infusion process.
- Strain the Oil: After a week or longer, strain the oil to remove the solid particles. You can use a fine mesh strainer, cheesecloth, or a coffee filter for this step.
- Store the Clove Oil: Transfer the strained clove oil into a clean, dark glass bottle with a tight-fitting lid. Dark glass helps protect the oil from light, preserving its potency.
- Label and Store: Label the bottle with the contents and the date. Store the clove oil in a cool, dark place. Properly stored, homemade clove oil can last for several months.
It’s important to note that while homemade clove oil can be a natural remedy, it may not be as concentrated or standardized as commercially produced essential oils. Exercise caution when using it, and if you experience any adverse reactions, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you’re using this oil for oral health purposes, make sure it is safe for oral use.
FAQ
Hi…Just have a look at this also!